1. Metabolic Conditions (Most Common)
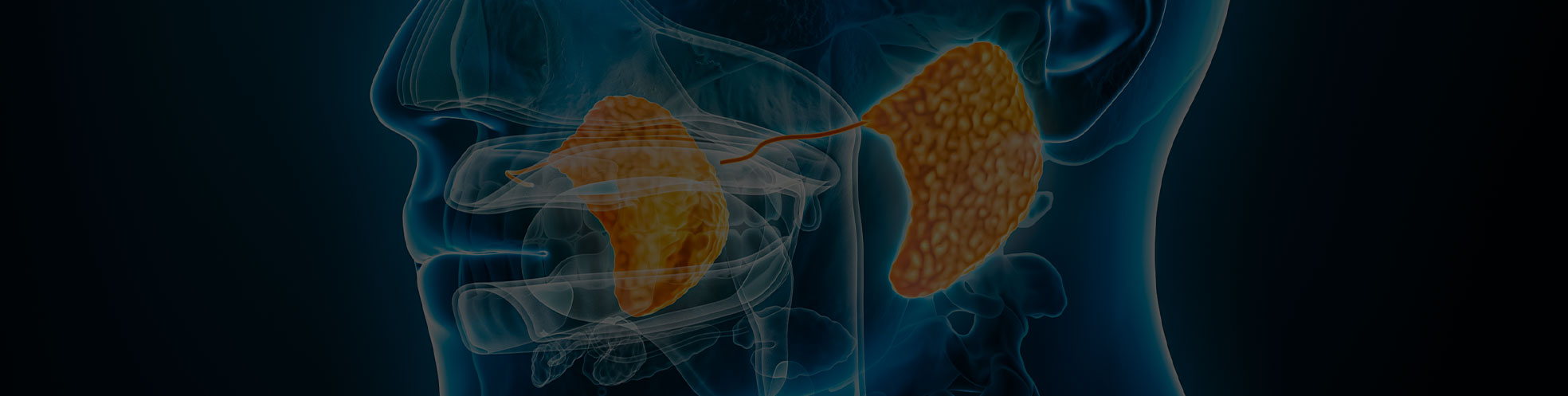
The most frequent cause of painless bilateral parotid enlargement is sialosis (also called sialadenosis).
- It is not an infection or a tumor
- The exact cause is unclear
- It is often linked to metabolic or nutritional issues
2. Autoimmune Diseases
Sjögren’s syndrome is a condition where the immune system attacks the salivary glands. People may also experience:
- Dry mouth
- Dry eyes
- Fatigue
Another inflammatory condition, sarcoidosis, can also cause parotid swelling, although it is less common.
3. Viral Infections
- Mumps can cause parotid swelling, but this is now rare due to vaccination
- HIV may cause cysts in the parotid glands, leading to long-term enlargement
4. Medications
Some medications can affect saliva production and cause the glands to swell, including:
- Antipsychotic medications
- Anticholinergic drugs
If swelling begins after starting a new medication, this may be a contributing factor.
5. Eating Disorders
Bulimia is a known cause of bilateral parotid gland enlargement. Repeated vomiting can overstimulate the salivary glands, leading to visible swelling over time. This is often an unexpected and devastating consequence of eating disorders.
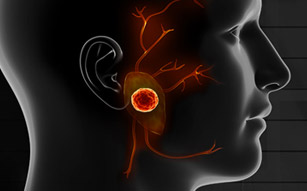
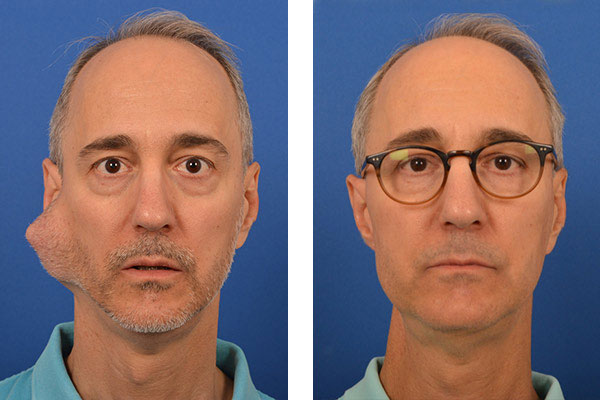
6. Tumors (Very Rare)
Tumors affecting both parotid glands at the same time are extremely rare. When tumors are present, scans usually show clear masses rather than general swelling of the glands.
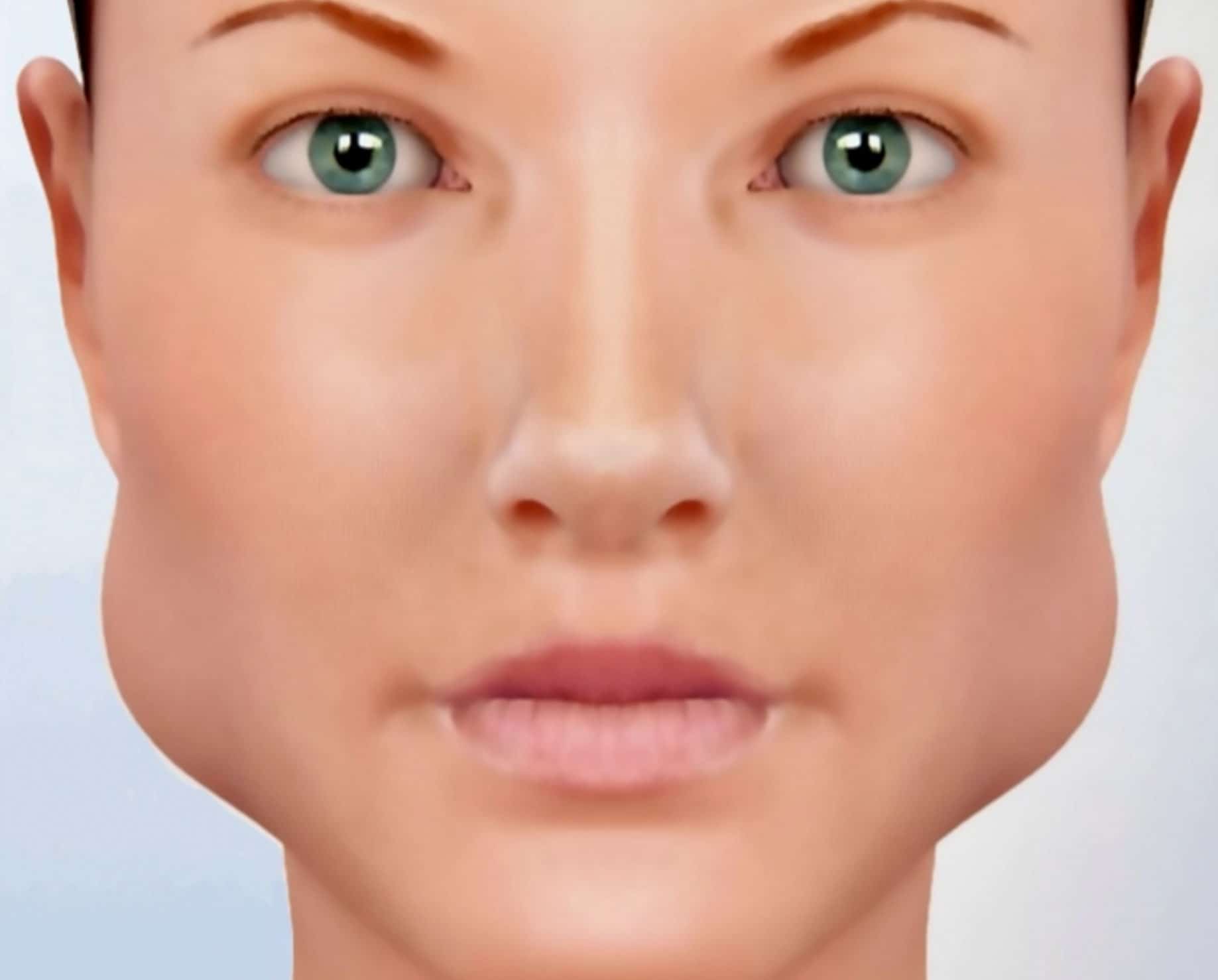
Is Bilateral Parotid Enlargement Painful?
In many cases, it is painless. Painless swelling is more commonly associated with metabolic, autoimmune, or medication-related causes rather than infection.
When Should You See a Doctor?
You should seek medical advice if you notice:
- Persistent swelling on both sides of the face
- Changes in facial appearance
- Facial pain
- Dry mouth or dry eyes
- Swelling that does not improve over time
An ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist can perform a full evaluation, which may include blood tests or imaging, to identify the cause and rule out serious
conditions.