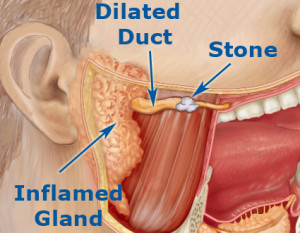
Parotid stones develop when chemicals,
debris and calcium build up in the salivary and parotid glands, blocking the duct and causing swelling, inflammation and infection.









debris and calcium build up in the salivary and parotid glands, blocking the duct and causing swelling, inflammation and infection.
Although the exact cause of this painful condition is unknown, experts do know that certain individuals are more at risk of developing stones than others. For example, stones are more likely to affect individuals who are elderly, suffer from gout or kidney disease, or have undergone head and neck radiotherapy.
Additional risk factors for developing parotid and salivary gland stones include dehydration, poor eating, trauma to the salivary glands and certain medications including blood pressure, psychiatric and bladder control drugs.
Although many individuals with parotid and salivary gland stones are asymptomatic, some patients may present the following symptoms:
After performing a physical examination and CT scan to provide a definitive diagnosis, Dr. Larian will thoroughly explain your treatment options depending on the location of the stones.
When a stone is located in the main substance of the gland, Dr. Larian will first recommend conservative treatment measures, such as increased water intake and massaging of the area. However, if those measures prove ineffective, he may recommend the surgical removal of the entire gland. If the stones are located in the duct, at the outermost portion, they can commonly be squeezed out. However, if they occur deep within the duct, they may require surgical removal with a sialoendoscopy procedure.
Regardless of the treatment plan Dr. Larian recommends, he and his team will use the most minimally invasive techniques available to successfully remove the stones and restore an improved quality of life.
Sialadenitis — or salivary gland inflammation — is a painful bacterial infection that most commonly occurs in older adults with parotid stones, although it may also affect newborn babies. The condition typically affects the parotid gland and occurs when the duct into the mouth becomes blocked, creating a painful lump and the drainage of foul-tasting pus into the mouth.
Treatment options for sialadenitis depend on whether the condition is acute, chronic or recurrent. The acute form comes on quickly with swelling, redness and pain, and may require antibiotics and other treatment measures. Common symptoms include swelling, reddened skin, low-grade fever, malaise, leucoytosis, edema of the cheek and drainage from the affected duct.
The chronic form of sialadenitis develops when the ducts are blocked due to stones and scarring. In these cases, symptoms occur after eating, due to the patient’s saliva backing up into the gland to cause swelling and pain. Although the symptoms will usually dissipate within a few hours, they will recur again after the next meal. If the patient’s chronic sialadenitis is very symptomatic and interferes with their quality of life, Dr. Larian may recommend the surgical removal of the gland through a superficial parotidectomy or submandibular gland incision.

Led by board-certified parotid surgeon, Dr. Babak Larian, our team of specialists has decades of experience successfully diagnosing and treating diseases of the parotid glands with minimally invasive procedures. Distinguished by our compassionate care and cutting-edge techniques, the CENTER has developed a reputation for delivering the best parotid tumor surgery available.