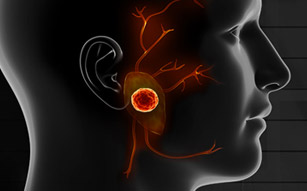
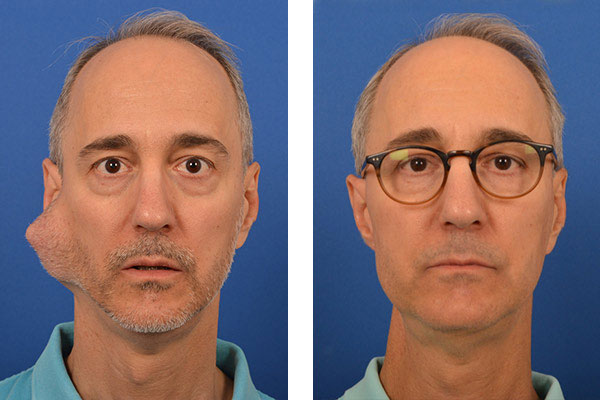
A mucocele is a cyst-like lesion in your mouth…
…most commonly found at the surface of the lower lip. It can also be found on the inner side of the cheek, on the anterior ventral tongue, and on the floor of the mouth. When found on the floor of the mouth, the mucocele is referred to as a ranula. A ranula is generally quite large, and often caused by a blocked submandibular duct. If you suspect you may be dealing with this condition, it’s best to speak with Dr. Larian and his group of experts at the CENTER, where you will be provided with excellent and focused patient care as well as a team approach to medicine not found elsewhere.