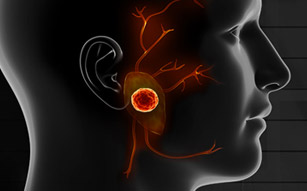
The tumors usually cause a firm, painless swelling in one of the salivary glands, and the size of the swelling gradually increases. Sometimes, these tumors also cause facial nerve palsy, which makes it difficult for patients to move one side of the face. At the CENTER for Advanced Parotid Surgery, Dr. Larian brings his patients optimal outcomes and success through his expert knowledge as well as utilizing a team of specialists who work with patients suffering from parotid tumors from day one.
Salivary gland tumors are abnormal cells growing in the ducts that drain the salivary glands
The most common type of salivary gland tumor is a slow-growing noncancerous (benign) parotid gland tumor, which gradually increases the size of the gland. However, some of these tumors can also be cancerous (malignant). The most common benign tumor is pleomorophic adenoma, and the most common malignant tumor is the mucoepidermoid carcinoma.
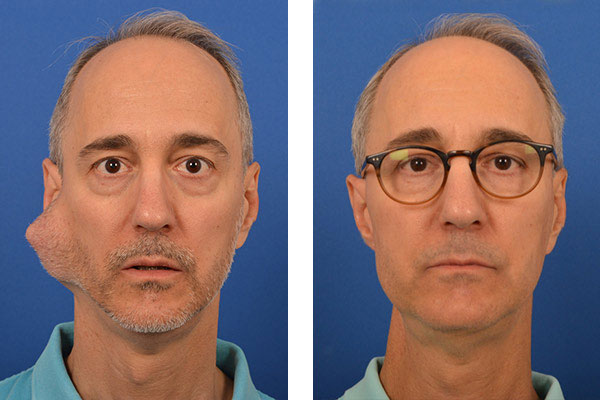
The recommended treatment is usually surgery to remove the affected salivary gland. If the tumor is benign, no other treatment is usually needed.
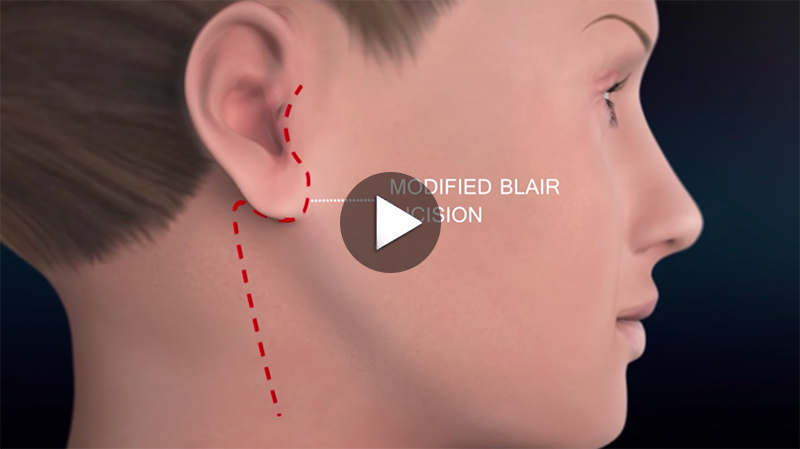
Parotid Surgery Animation
Types of tumors listed
- Pleomorphic adenoma
- Warthin’s tumor
- Mucoepidermoid Carinoma
- Acinic Cell Carcinoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Carcinoma Ex-Pleomorphic
- Metastasis from Other Cancers
Pleomorphic adenoma is, by far, the most common benign salivary gland tumor
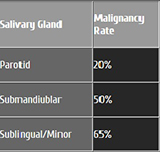
Accounting for as many as 80% of all such tumors. Although pleomorphic adenomas most commonly occur in the parotid gland, it may also be encountered in the submandibular, lingual, and minor salivary glands. Pleomorphic adenoma is the most common tumor in these glands, even though almost half of the tumors found in the minor salivary glands are malignant.
Warthin’s tumor is a type of benign tumor of the salivary glands
The gland most likely affected is the parotid gland. Only pleomorphic adenoma is a more common benign parotid tumor. Warthin’s tumor is slow growing, painless, and primarily affects older individuals. The tumor is bilateral, and highly unlikely to become malignant.
Mucoepidermoid Carinoma is an abnormal growth of tissue
Resulting from uncontrolled, progressive multiplication of cells, serving no physiological function.This is the most common type of salivary gland malignancy in adults, and most of them appear clinically as so called mixed tumors.
The tumor usually forms as a painless, slow-growing, fixed mass that is firm or hard. These tumors vary widely in duration, and sometimes go through a phase of accelerated growth immediately before clinical presentation.
Acinic Cell Carcinoma is a tumor most commonly found in the parotid gland
Presents itself as a slow growing mass. These tumors vary in their behavior, from locally aggressive to blatantly malignant, and are sometimes associated with pain or tenderness. Acinic cell carcinoma appears in all age groups, but presents at a younger median age (52 years) than most other salivary gland cancers.
is a rather rare type of cancer that can exist in many different body sites
Although most commonly in the salivary glands. It is the third most common malignant salivary gland tumor overall, and represents 28% of malignant submandibular gland tumors. This makes it the single most common malignant salivary gland tumor in this region.
Early lesions of the salivary glands present as painless masses of the mouth or face, and usually grow slowly. Advanced tumors, meanwhile, may present with pain and/or nerve paralysis.
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common form of non-melonoma skin cancer
Accounts for 90% of all head and neck cancers. Most squamous cell carcinomas are readily identified and removed in our office as a minor surgical procedure. Larger and more invasive lesions may, however, require aggressive surgical management, radiation therapy, or both.
Carcinoma Ex-Pleomorphic is a type of cancer that initially started off as a benign tumor
Although pleomorphic adenomas are benign parotid tumors, it has the potential to turn malignant. The incidence of malignant transformation increases with the duration of the tumor. Signals of malignant transformation include facial weakness, pain, skin invasion and fixation of mastoid tip, rapid growth, and parasthesia.
Metastasis from Other Cancers is cancer that has spread from the place where it first started
Treatment for metastatic cancer usually depends on the type of cancer, the size of it, location, and total number of metastatic tumors.
If you would like to schedule a consultation with salivary gland tumor expert Dr. Larian, give us a call at (310) 461-0300 today!
Next, learn about the facial paralysis risk associated with parotidectomy.